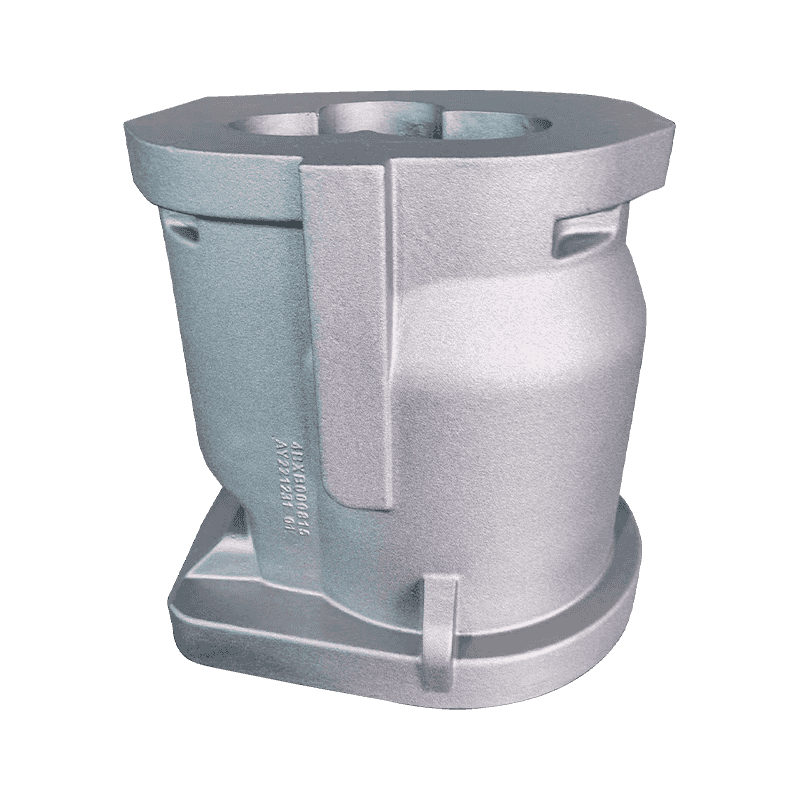
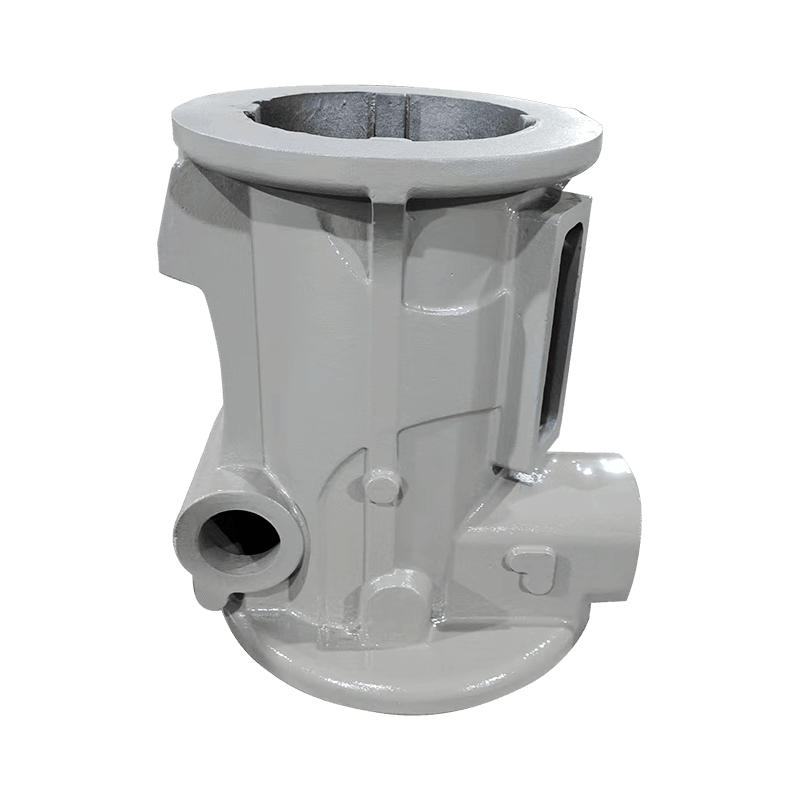
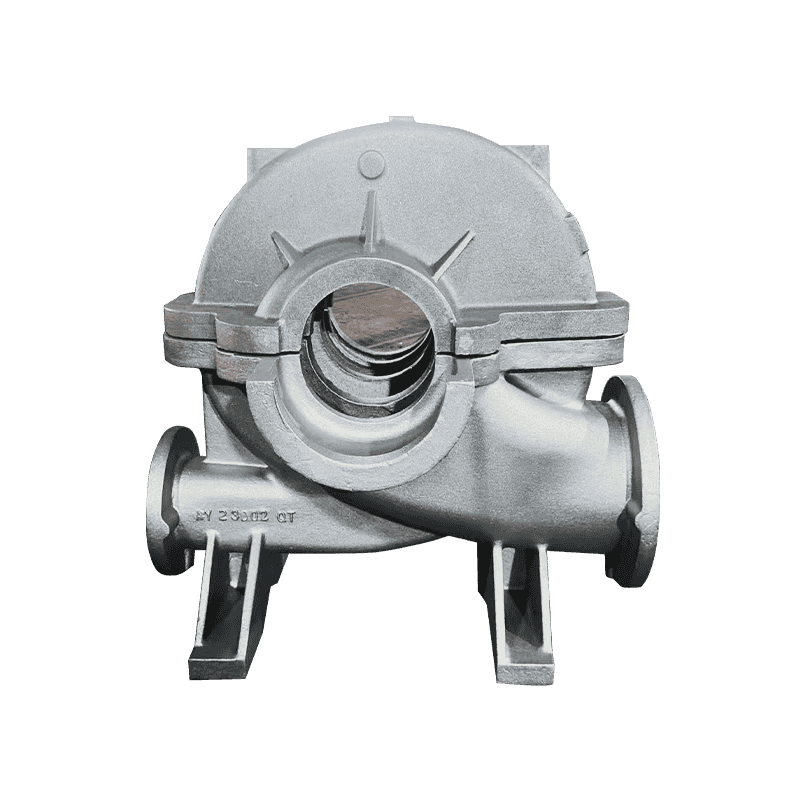
Digital casting technology for machine tool castings optimizes the design, production and quality control of castings by integrating advanced computer technology and data analysis. Here are some of the steps.
CAD Modeling
In the first step of digital casting, engineers use computer-aided design (CAD) software to create a detailed 3D model of the casting. CAD modeling is not just about drawing the geometry of the casting, but also involves structural optimization and functional verification of the design. Engineers can make various modifications and adjustments to the casting in a virtual environment to achieve the best design solution. Through CAD modeling, the size, shape and assembly requirements of the casting can be accurately defined, laying the foundation for subsequent simulation analysis.
Flow Analysis
Computer-aided engineering (CAE) software is used to simulate the flow of molten metal in the mold. Flow analysis can predict defects such as pores, inclusions or cold shuts that may occur during the casting process. By simulating different pouring speeds, pouring temperatures and pouring locations, engineers can identify and solve problems with uneven flow and optimize the pouring system design.
Cooling Analysis
Cooling analysis involves simulating the temperature distribution and cooling rate of the casting during the cooling process. The cooling process is critical to the final performance of the casting because it affects the microstructure and mechanical properties of the casting. Cooling analysis helps engineers predict the possible deformation and internal stress of the casting during the cooling process and adjust the cooling system design to ensure uniform cooling of the casting.
Stress analysis
Stress analysis is used to evaluate the stress distribution that the casting may be subjected to during use. By simulating the stress state of the casting under different working conditions, engineers can identify stress concentration areas and potential failure points. Stress analysis helps engineers optimize the design and ensure the reliability and stability of the casting under actual working conditions.